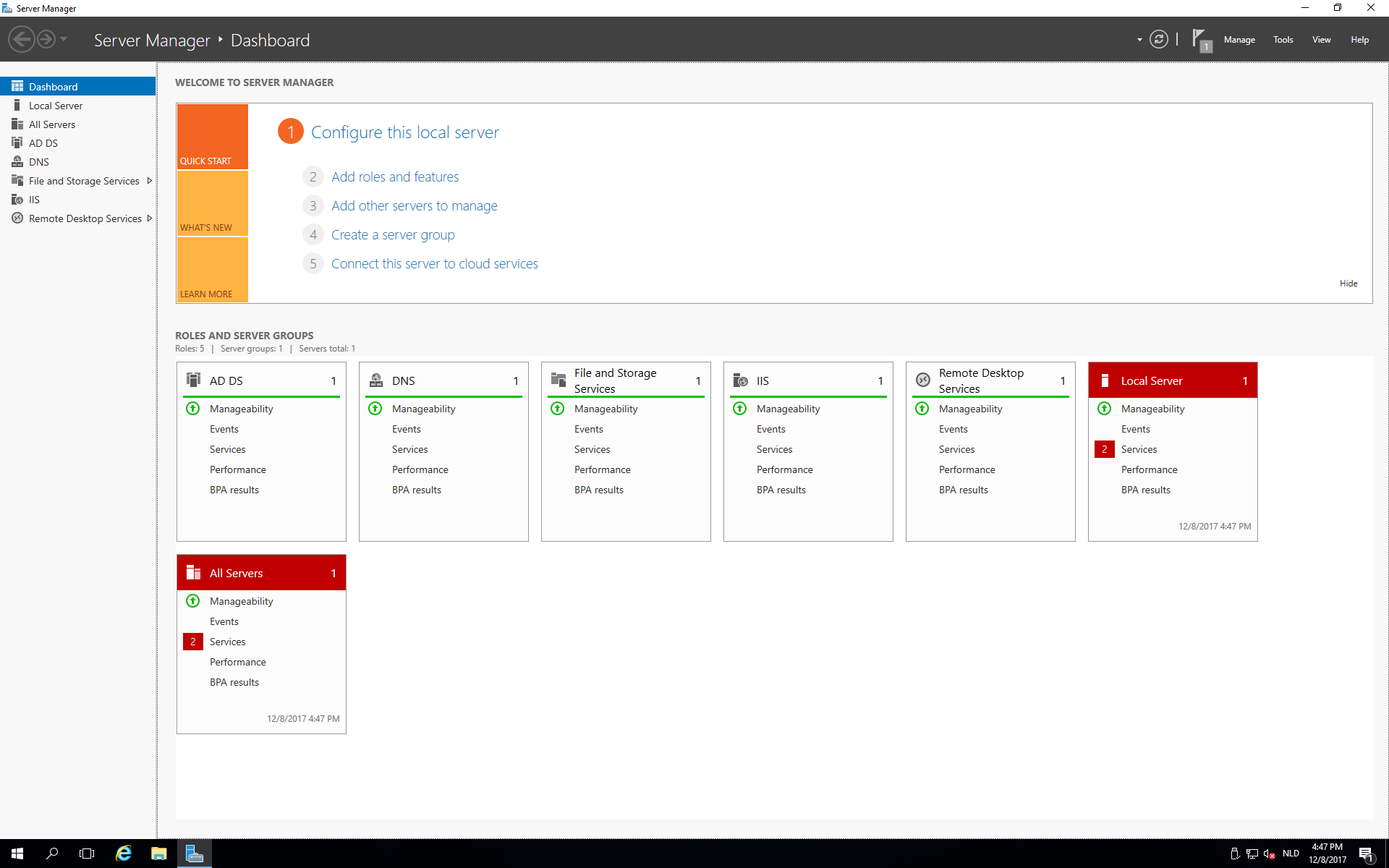
- Windows Server 2016 Essentials Remote Desktop Services
- Windows Server Essentials Remote Desktop Services Windows
- Windows Remote Desktop Services
- Remote Desktop Services Windows 10
The user has deployed Windows 2016 Essentials and completed the Access Anywhere wizard. It appears to deploy all the RDS roles, it configures it for per-user licensing and the essentials server is listed as the licensing server. There are no errors around the deployment other than the licensing notice. Licensing mode remains 'Remote Desktop for. Remote Web Access file sharing is the new feature added to the Small Business Server 2011 family. It allows users access shares and the files they contain on SBS server remotely. With file sharing in RWA you can: Upload and download files Create and delete folders underneath the.
On September 5, 2018 the Microsoft Windows Server Team announced via theWindows Server Blog that they are killing off Windows Server Essentials as it currently exists today:
While Microsoft will still be releasing an “Essentials” SKU for Windows Server 2019, it will be completely devoid of everything that we recognize as being part of Windows Server Essentials in its current form. Small Business Server MVP Robert Pearman summarizes the upcoming release of Windows Server 2019 Essentials as follows:
“With the release of Server 2019 Essentials, the end of an era has been reached. Gone are the wizards and tools designed for the small business owner.
Gone is the Remote Web Access feature.
Gone is the Essentials Connector.
Gone is Client PC Backup.
Gone is Office 365 Integration.
Gone, is the Dashboard.
Gone, indeed, is the Essentials Role.
All that remains of Essentials, is the name Essentials and the licensing limits of the Essentials SKU, of 25 client access licenses.
What we are presented with, is now more in line with Windows foundation server from several years ago.“
Basically, Microsoft is releasing their first (and last) non-essentials Windows Server Essentials release that is completely gutted of anything even remotely resembling Windows Server Essentials as we currently know it. And obviously, without the underlying “Essentials” bits, there can be no more new WSE RemoteApp or WSE WorkFolders product releases going forward.
It’s been a fun run, but we have indeed now come to the end of an era for Windows Server Essentials.
My suggestion to those who want to continue running an on-premises Essentials server would be to grab up as many Windows Server 2016 (Standard, Datacenter, or Essentials) licenses as you possibly can (before they’re all gone), and then ride it out with that particular version for as long as Microsoft will be providing support for it (see: Windows Server 2016 Essentials servicing timeline).
Le Roi Est Mort, Vive Le Roi!
UPDATE #1: It’s quite obvious that Microsoft wants small businesses to dump Windows Server Essentials and move to the(ir) cloud, but personally, I don’t want my business (nor personal) data on anyone’s cloud. See:
US-CERT – Common Risks of Using Business Apps in the Cloud
UPDATE #2: Fear not, as all may not be lost after all… See:
Installing Windows Server Essentials Experience On Windows server 2019 / 2022
Comments are closed.
Products
Windows Server Solutions Add-ins
Shopping Cart
-->Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016
This article describes the roles within a Remote Desktop Services environment.
Remote Desktop Session Host
The Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host) holds the session-based apps and desktops you share with users. Users get to these desktops and apps through one of the Remote Desktop clients that run on Windows, MacOS, iOS, and Android. Users can also connect through a supported browser by using the web client.
You can organize desktops and apps into one or more RD Session Host servers, called 'collections.' You can customize these collections for specific groups of users within each tenant. For example, you can create a collection where a specific user group can access specific apps, but anyone outside of the group you designated won't be able to access those apps.
For small deployments, you can install applications directly onto the RD Session Host servers. For larger deployments, we recommend building a base image and provisioning virtual machines from that image.
You can expand collections by adding RD Session Host server virtual machines to a collection farm with each RDSH virtual machine within a collection assigned to same availability set. This provides higher collection availability and increases scale to support more users or resource-heavy applications.
In most cases, multiple users share the same RD Session Host server, which most efficiently utilizes Azure resources for a desktop hosting solution. In this configuration, users must sign in to collections with non-administrative accounts. You can also give some users full administrative access to their remote desktop by creating personal session desktop collections.
You can customize desktops even more by creating and uploading a virtual hard disk with the Windows Server OS that you can use as a template for creating new RD Session Host virtual machines.
For more information, see the following articles:
Remote Desktop Connection Broker
Remote Desktop Connection Broker (RD Connection Broker) manages incoming remote desktop connections to RD Session Host server farms. RD Connection Broker handles connections to both collections of full desktops and collections of remote apps. RD Connection Broker can balance the load across the collection's servers when making new connections. If RD Connection Broker is enabled, using DNS round robin to RD Session Hosts for balacing servers is not supported. If a session disconnects, RD Connection Broker will reconnect the user to the correct RD Session Host server and their interrupted session, which still exists in the RD Session Host farm.
You'll need to install matching digital certificates on both the RD Connection Broker server and the client to support single sign-on and application publishing. When developing or testing a network, you can use a self-generated and self-signed certificate. However, released services require a digital certificate from a trusted certification authority. The name you give the certificate must be the same as the internal Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the RD Connection Broker virtual machine.
You can install the Windows Server 2016 RD Connection Broker on the same virtual machine as AD DS to reduce cost. If you need to scale out to more users, you can also add additional RD Connection Broker virtual machines in the same availability set to create an RD Connection Broker cluster.
Before you can create an RD Connection Broker cluster, you must either deploy an Azure SQL Database in the tenant's environment or create an SQL Server AlwaysOn Availability Group.
For more information, see the following articles:
- SQL database in Desktop hosting service.
Remote Desktop Gateway
Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) grants users on public networks access to Windows desktops and applications hosted in Microsoft Azure's cloud services.

The RD Gateway component uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt the communications channel between clients and the server. The RD Gateway virtual machine must be accessible through a public IP address that allows inbound TCP connections to port 443 and inbound UDP connections to port 3391. This lets users connect through the internet using the HTTPS communications transport protocol and the UDP protocol, respectively.
The digital certificates installed on the server and client have to match for this to work. When you're developing or testing a network, you can use a self-generated and self-signed certificate. However, a released service requires a certificate from a trusted certification authority. The name of the certificate must match the FQDN used to access RD Gateway, whether the FQDN is the public IP address' externally facing DNS name or the CNAME DNS record pointing to the public IP address.
For tenants with fewer users, the RD Web Access and RD Gateway roles can be combined on a single virtual machine to reduce cost. You can also add more RD Gateway virtual machines to an RD Gateway farm to increase service availability and scale out to more users. Virtual machines in larger RD Gateway farms should be configured in a load-balanced set. IP affinity isn't required when you're using RD Gateway on a Windows Server 2016 virtual machine, but it is when you're running it on a Windows Server 2012 R2 virtual machine.
For more information, see the following articles:

Remote Desktop Web Access
Remote Desktop Web Access (RD Web Access) lets users access desktops and applications through a web portal and launches them through the device's native Microsoft Remote Desktop client application. You can use the web portal to publish Windows desktops and applications to Windows and non-Windows client devices, and you can also selectively publish desktops or apps to specific users or groups.
RD Web Access needs Internet Information Services (IIS) to work properly. A Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) connection provides an encrypted communications channel between the clients and the RD Web server. The RD Web Access virtual machine must be accessible through a public IP address that allows inbound TCP connections to port 443 to allow the tenant's users to connect from the internet using the HTTPS communications transport protocol.

Matching digital certificates must be installed on the server and clients. For development and testing purposes, this can be a self-generated and self-signed certificate. For a released service, the digital certificate must be obtained from a trusted certification authority. The name of the certificate must match the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) used to access RD Web Access. Possible FQDNs include the externally facing DNS name for the public IP address and the CNAME DNS record pointing to the public IP address.
For tenants with fewer users, you can reduce costs by combining the RD Web Access and Remote Desktop Gateway workloads into a single virtual machine. You can also add additional RD Web virtual machines to an RD Web Access farm to increase service availability and scale out to more users. In an RD Web Access farm with multiple virtual machines, you'll have to configure the virtual machines in a load-balanced set.
Windows Server 2016 Essentials Remote Desktop Services
For more information about how to configure RD Web Access, see the following articles:
Windows Server Essentials Remote Desktop Services Windows
Remote Desktop Licensing
Activated Remote Desktop Licensing (RD Licensing) servers let users connect to the RD Session Host servers hosting the tenant's desktops and apps. Tenant environments usually come with the RD Licensing server already installed, but for hosted environments you'll have to configure the server in per-user mode.
Windows Remote Desktop Services
The service provider needs enough RDS Subscriber Access Licenses (SALs) to cover all authorized unique (not concurrent) users that sign in to the service each month. Service providers can purchase Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services directly, and can purchase SALs through the Microsoft Service Provider Licensing Agreement (SPLA) program. Customers looking for a hosted desktop solution must purchase the complete hosted solution (Azure and RDS) from the service provider.
Remote Desktop Services Windows 10
Small tenants can reduce costs by combining the file server and RD Licensing components onto a single virtual machine. To provide higher service availability, tenants can deploy two RD License server virtual machines in the same availability set. All RD servers in the tenant's environment are associated with both RD License servers to keep users able to connect to new sessions even if one of the servers goes down.
For more information, see the following articles:
